brochure des produits bioactifs MCE
catalogue des inhibiteurs, bibliothèques de criblage, et protéines

Contenu du document
MCE - Master of Bioactive Molecules
Inhibitors • Screening Libraries • Proteins
Dark Quenchers
- BHQ1
- BHQ2
- BHQ3
- DabcyI
- Eclipse
Related popular products are listed below:
- HY-150741 - ODN 2216: A TLR-9 agonist, used as vaccine adjuvant. Type: CpG ODN
- HY-150751 - ODN TTAGGG: A TLR9, AIM2 and cGAS antagonist, used in the study of lupus erythematosus and other related autoimmune diseases. Type: Oligonucleotides
Degenerate Bases
IUB Base Codes: B=C/G/T, D=A/G/T, H=A/C/T, I=Universal Base, K=G/T, M=A/C, N=A/C/G/T, R=A/G, S=C/G, V=A/C/G, W=A/T, Y=C/T
RNA therapy: A Break-through for ‘Undruggable-target’ Limitations
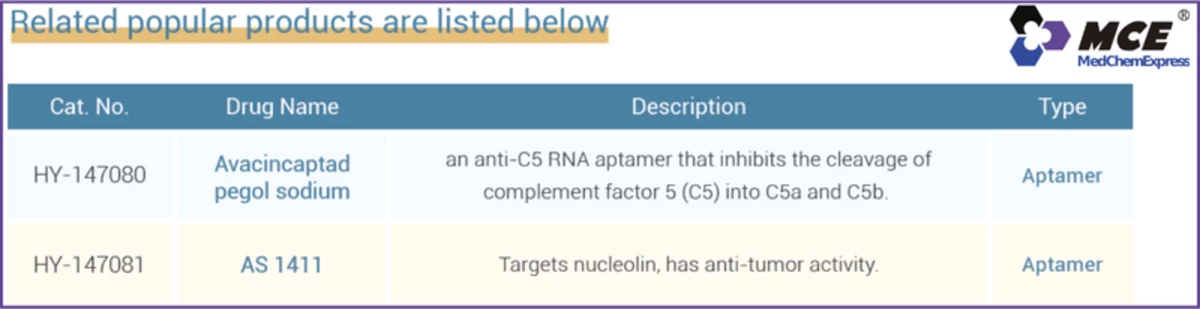
- HY-147080 - Avacincaptad pegol sodium: An anti-C5 RNA aptamer that inhibits the cleavage of complement factor 5 (C5) into C5a and C5b. Type: Aptamer
- HY-147081 - AS 1411: Targets nucleolin, has anti-tumor activity. Type: Aptamer
- HY-132588 - Lumasiran: Reduces hepatic oxalate production by targeting glycolate oxidase. Type: siRNA
Attachment Chemistry / Linkers Modifications
- Acrydite
- Aldehyde
- Alkyne
- Amino
- Azide
- Biotin
- Carboxy
- COOH
- DBCO
- Digoxin
- Maleimide
- Thiol
Modifications of Spacers
- C3 Spacer
- C6 Spacer
- C12 Spacer
- dSpacer
- PC-linker
- Spacer 18
- Spacer 9
Modified Bases
- 2' Fluoro bases
- 2-O-Methyl Base
- 2-Aminopurine
- 5-Aza-2'-dC
- 5-Bromo dU
- 5-Hydroxymethyl dC
- 5-Methyl dC
- 5-Nitroindole
- 8-Oxo deoxyguanosine
- deoxylnosine
- DeoxyUridine
- Dideoxycytidine
- Inverted dG
- Inverted dT
- LNA
- N6 Methyl dA
- phosphorothioate
- Phosphorylation
- Pyrrolo-dC
MCE Oligonucleotide Synthesis Services
MCE owns a professional team and state-of-the-art facilities in the production and analysis of oligonucleotides. MCE can synthesize oligonucleotides to suit your specific needs, carry out related testing procedures (purity, structure and stability analysis), and ensure the accuracy and reproducibility of data with high-quality and efficient services.