application note sur le séquençage de nouvelle génération par microsynth
note d'application sur l'analyse épidémiologique génomique
Contenu du document
The Swiss DNA Company
Application Note · Next Generation Sequencing
Genomic Epidemiology Analysis
- Determine the sequence type of microbial isolates
- Screen for resistance, virulence, and mycotoxin genes
- Identify genetic variations that lead to pathogenicity
Introduction
Genomic epidemiology studies are useful to support public health, combat infectious diseases, maintain food safety, or establish sustainable production lines. To support our customers in these diverse applications, Microsynth has developed a genomic epidemiology pipeline that addresses numerous scientific topics concerning your epidemiology project:
- Resolve the taxonomy of individual species or sequence type (ST)
- Identify resistance, virulence and mycotoxin genes
- Detect multidrug resistant bacterial pathogens (MDR)
- Detect acquired mutations and assess their potential functional effects
- Establish a population-level profiling and comparison of antimicrobial resistance
Our genomic epidemiology analysis pipeline is based on next generation whole genome sequencing. The generated data and knowledge will support production lines, can be used to track transmission, or used in pathogen outbreak surveillance, to just name a few examples. At Microsynth, we will guide you through the whole analysis to assure you will achieve your goals.
Microsynth’s Competences and Services
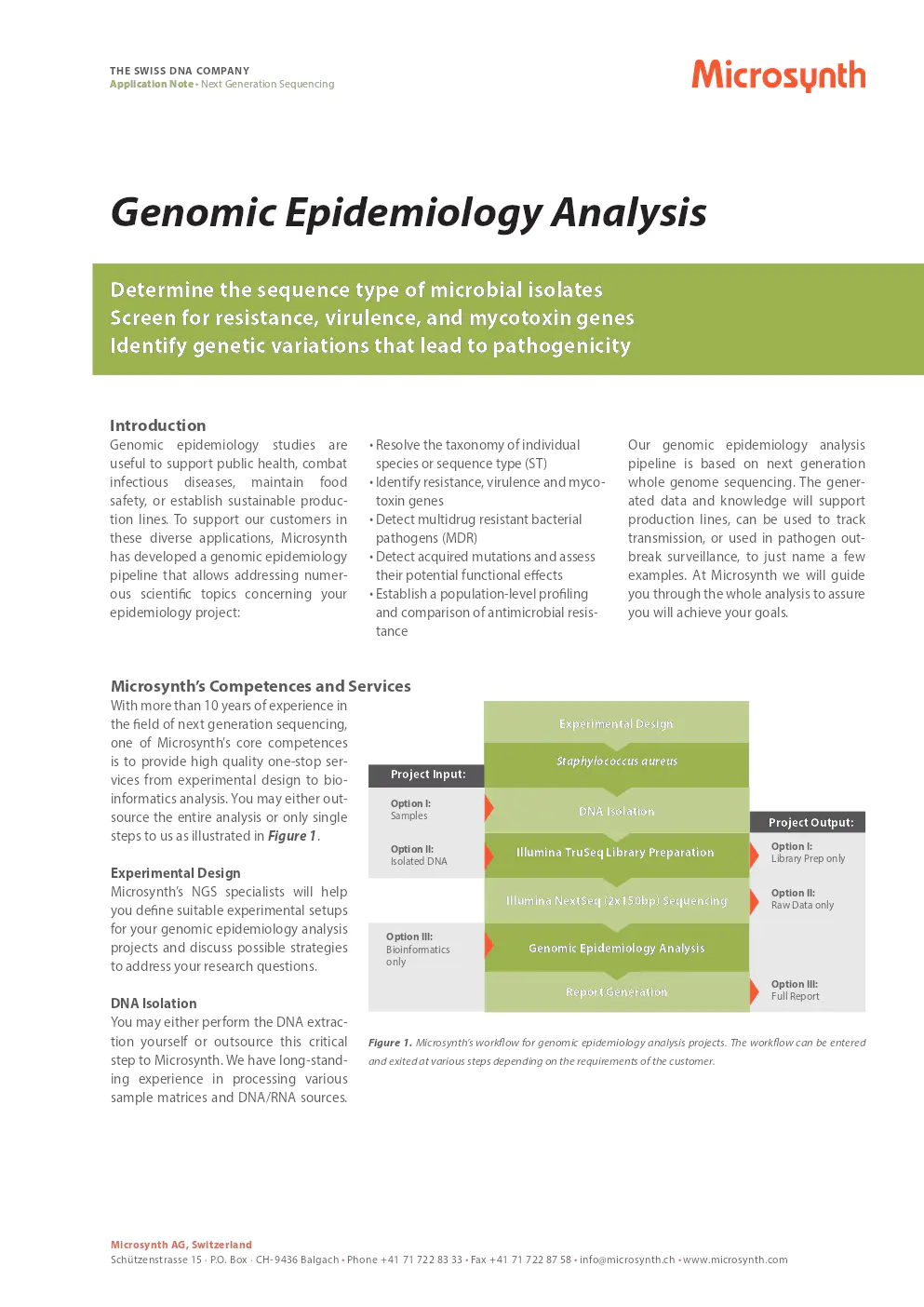
With more than 10 years of experience in the field of next generation sequencing, one of Microsynth’s core competences is to provide high quality one-stop services from experimental design to bioinformatics analysis. You may either outsource the entire analysis or only single steps to us as illustrated in Figure 1.
Experimental Design
Microsynth’s NGS specialists will help you define suitable experimental setups for your genomic epidemiology analysis projects and discuss possible strategies to address your research questions.
DNA Isolation
You may either perform the DNA extraction yourself or outsource this critical step to Microsynth. We have long-standing experience in processing various sample matrices and DNA/RNA sources.
Library Preparation and Sequencing
Following a quality check of your samples, Microsynth will build Illumina libraries including specific adaptors with barcodes. Depending on the experimental design, the libraries are pooled and sequenced either on the Illumina MiSeq or NextSeq 500/550. These flexible platforms allow for optimal sequencing depending on the number of samples and on the required read length.
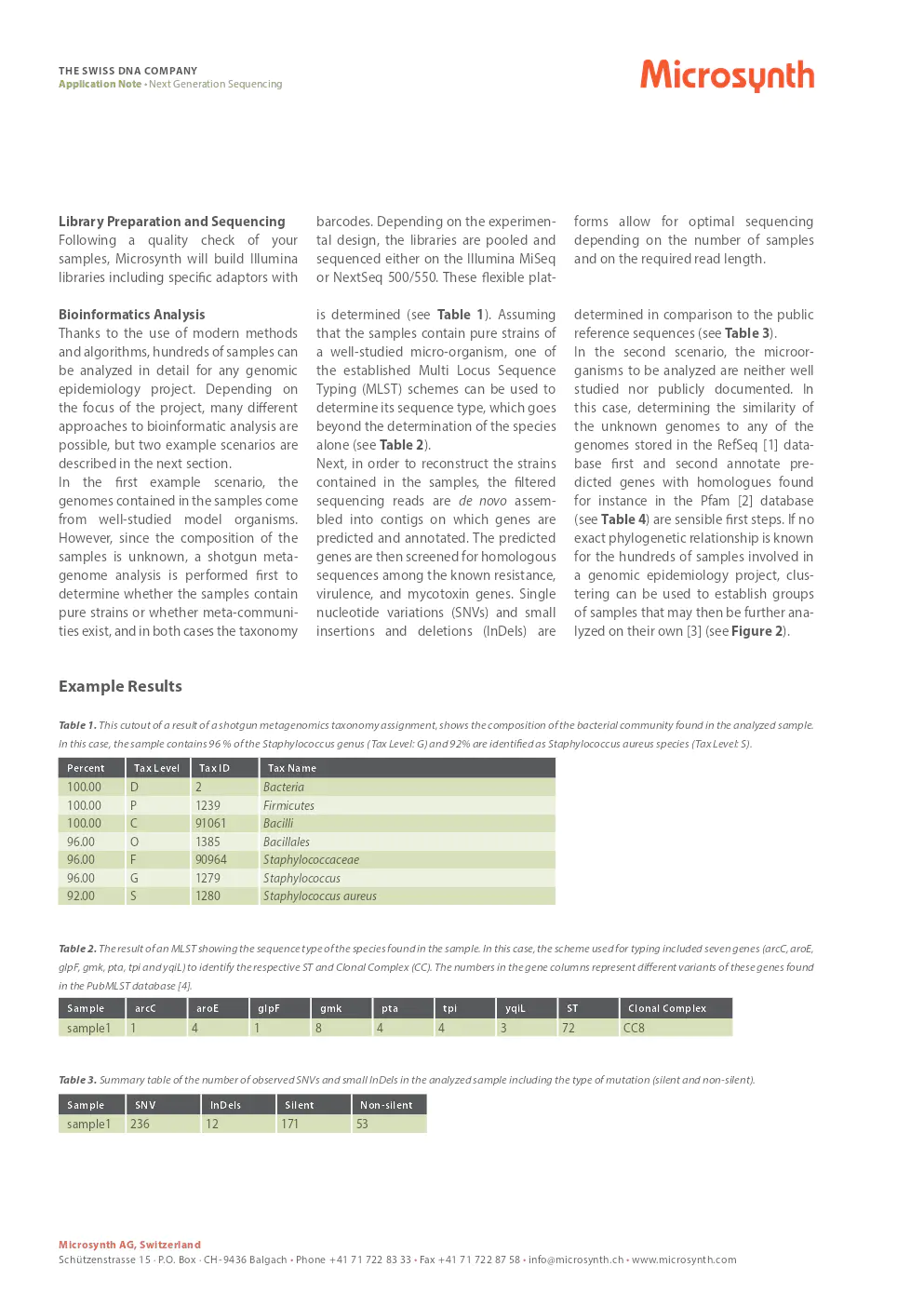
Bioinformatics Analysis
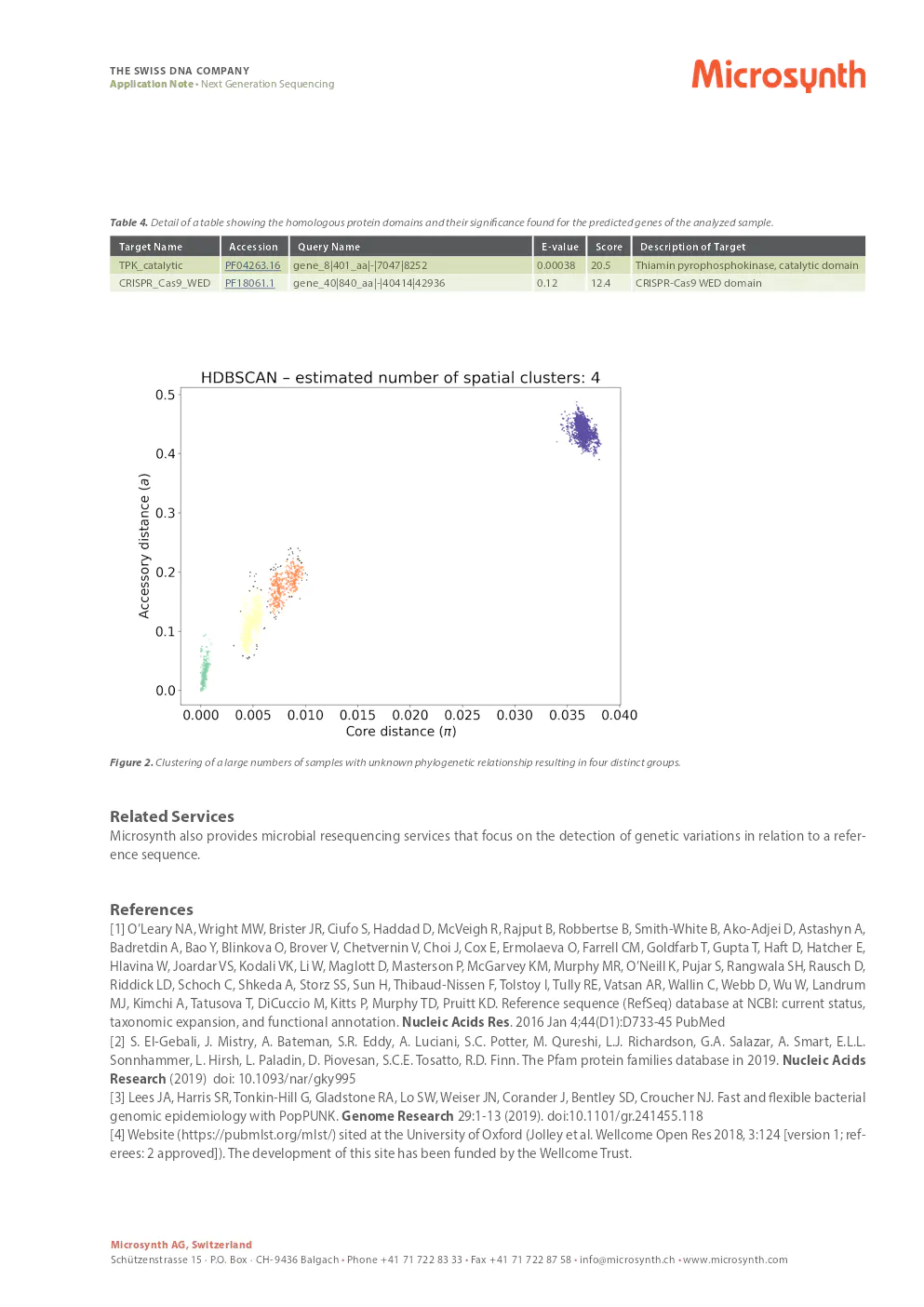
Thanks to the use of modern methods and algorithms, hundreds of samples can be analyzed in detail for any genomic epidemiology project. Depending on the focus of the project, many different approaches to bioinformatic analysis are possible, but two example scenarios are described in the next section.
Example Results
Table 1. This cutout of a result of a shotgun metagenomics taxonomy assignment shows the composition of the bacterial community found in the analyzed sample. In this case, the sample contains 96% of the Staphylococcus genus (Tax Level: G) and 92% are identified as Staphylococcus aureus species (Tax Level: S).
- Percent: 100.00
- Tax Level: D
- Tax ID: 2
- Tax Name: Bacteria
- Percent: 100.00
- Tax Level: P
- Tax ID: 1239
- Tax Name: Firmicutes
- Percent: 100.00
- Tax Level: C
- Tax ID: 91061
- Tax Name: Bacilli
- Percent: 96.00
- Tax Level: O
- Tax ID: 1385
- Tax Name: Bacillales
- Percent: 96.00
- Tax Level: F
- Tax ID: 90964
- Tax Name: Staphylococcaceae
- Percent: 96.00
- Tax Level: G
- Tax ID: 1279
- Tax Name: Staphylococcus
- Percent: 92.00
- Tax Level: S
- Tax ID: 1280
- Tax Name: Staphylococcus aureus
Table 2. The result of an MLST showing the sequence type of the species found in the sample. In this case, the scheme used for typing included seven genes (arcC, aroE, glpF, gmk, pta, tpi and yqiL) to identify the respective ST and Clonal Complex (CC). The numbers in the gene columns represent different variants of these genes found in the PubMLST database [4].
- Sample: sample1
- arcC: 1
- aroE: 4
- glpF: 1
- gmk: 8
- pta: 4
- tpi: 4
- yqiL: 3
- ST: 72
- Clonal Complex: CC8
Table 3. Summary table of the number of observed SNVs and small InDels in the analyzed sample including the type of mutation (silent and non-silent).
- Sample: sample1
- SNV: 236
- InDels: 12
- Silent: 171
- Non-silent: 53
Related Services
Microsynth also provides microbial resequencing services that focus on the detection of genetic variations in relation to a reference sequence.
References
- [1] O’Leary NA, Wright MW, Brister JR, et al. Reference sequence (RefSeq) database at NCBI: current status, taxonomic expansion, and functional annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jan 4;44(D1):D733-45 PubMed
- [2] S. El-Gebali, J. Mistry, A. Bateman, et al. The Pfam protein families database in 2019. Nucleic Acids Research (2019) doi: 10.1093/nar/gky995
- [3] Lees JA, Harris SR, Tonkin-Hill G, et al. Fast and flexible bacterial genomic epidemiology with PopPUNK. Genome Research 29:1-13 (2019). doi:10.1101/gr.241455.118
- [4] Website (https://pubmlst.org/mlst/) sited at the University of Oxford (Jolley et al. Wellcome Open Res 2018, 3:124 [version 1; referees: 2 approved]). The development of this site has been funded by the Wellcome Trust.
Microsynth AG, Switzerland
Schützenstrasse 15 · P.O. Box · CH-9436 Balgach · Phone +41 71 722 83 33 · Fax +41 71 722 87 58 · info@microsynth.ch · www.microsynth.com